🔬 تکنیک FISH برای تعیین وضعیت HER2 در سرطان پستان
نویسنده: بهنیا صادقی
هدف از انجام آزمایش Test HER2 چیست؟
- 12فروردين 1399
HER2 کوتاه شده عبارت گیرنده عامل رشد پوستی انسانی ۲ است که با عنوان ERBB2 نیز خوانده می شود. در برخی از سرطان ها، بویژه سرطان سینه یا سرطان های معده و نای، سلول های تومور دارای نسخه های اضافی از ژن و مقادیر اضافی از پروتئین هایی هستند که تولید می شود. تومورها در این گروه با عنوان HER2-مثبت خوانده شده و می توانند گسترش یابند و بطور متفاوتی نسبت به تومورهای HER2-منفی به درمان پاسخ دهند. آزمایش HER2 که بر روی نمونه های تومور انجام می شود نشانگر اینست که آیا شخص دارای سرطان HER2-مثبت است یا خیر.
در سلول های طبیعی، ژن HER2 پروتئینی را رمزگذاری می کند که به توسعه رشد سلولی کمک می نماید. زمانی که یک جهش منجر به نسخه های بسیار زیاد درون یک سلول می شود (تکثیر)، در این حالت HER2 پروتئین زیادی را تولید می کند و موجب می شود HER2 به عنوان یک ژن سرطانی عمل کند، بدین معنی که می تواند موجب رشد غیرقابل کنترل و سرطانی شود. این در حدود یک مورد از هر پنج سرطان سینه رخ می دهد و می تواند در سرطان های دیگری مثل سرطان معده و نای نیز اتفاق بیافتد.
انجمن تومورشناسی بالینی آمریکا (ASCO) و کالج آسیب شناسی آمریکا (CAP) بطور مشترک توصیه می نمایند که تومورهای همه افراد مبتلا به سرطان سینه گسترش یافته یا عود کننده تحت آزمایش HER2 قرار بگیرد. سرطان سینه گسترش یافته نوعی از سرطان است که از مجرای موجود در سینه به بخش های دیگر آن یا بافت ها یا اندام های دیگر گسترش پیدا کند. بطور مشابه ASCO و CAP توصیه می کنند که بیماران مبتلا به سرطان های خاص معده و نای (غیرقابل جراحی و پیشرونده یا عود کننده و یا متاستاز) که ممکن است از درمان HER2 نفع ببرند، باید تحت این آزمایش قرار بگیرند.
برای تعیین مثبت بودن تومور برای HER2، یک نمونه از تومور مورد آزمایش قرار می گیرد. دو روش برای آزمایش وضعیت HER2 وجود دارد:
-Immunohistochemistry (IHC) که مقدار پروتئین HER2 موجود را اندازه گیری می کند. …
مركز جامع خدمات ژنتيك و شركت ژنهاي طلايي تمامي خدمات مربوط به تست سرطان سينه را انجام ميدهد خدمات و اموزش و تكنيك و جوابدهي به بيماران و مراجعين
1. مقدمه: اهمیت تعیین وضعیت HER2 در سرطان پستان
ژن ERBB2 یا همان HER2، یکی از ژنهای مهم در سرطان پستان است که تولیدکنندهی گیرندهی تیروزین کینازی از خانواده فاکتور رشد اپیدرمال (EGFR) میباشد. افزایش بیان یا تکثیر ژن HER2، در حدود 15–20٪ از سرطانهای پستان دیده میشود و با پیشرفت سریعتر بیماری و پیشآگهی نامطلوبتر همراه است.
2. روشهای تشخیصی برای بررسی HER2
2.1. ایمونوهیستوشیمی (IHC)
در این روش، میزان پروتئین HER2 روی سطح سلولهای سرطانی ارزیابی میشود:
- IHC 0 یا 1+: HER2 منفی
- IHC 2+: مرزی (نیازمند تست تأییدی)
- IHC 3+: HER2 مثبت
- 🔬 توضیح علمی:
بر اساس دستورالعملهای ASCO/CAP (کالج پاتولوژی آمریکا و انجمن انکولوژی بالینی)، وقتی IHC = 3+ گزارش میشود، یعنی رنگپذیری غشای سلولها قوی، کامل و در بیش از ۱۰٪ سلولهای توموری دیده شده است. در این حالت، معمولاً تومور HER2 مثبت تلقی میشود و دیگر نیاز به FISH ندارد.
اما: - در یک درصد کمی از موارد (معمولاً زیر 5٪) ممکن است IHC 3+ کاذب گزارش شود.
- این خطاها معمولاً ناشی از:
- آرتیفکتهای تکنیکی (نمونهبرداری، فیکساسیون، یا رنگآمیزی)
- تفسیر نادرست توسط پاتولوژیست
- وجود ناهمگنی (heterogeneity) در بیان HER2 داخل تومور
- 📌 در این شرایط، اگر نتایج درمانی مهم باشند یا شکی در صحت گزارش وجود داشته باشد، انجام تست FISH یا روشهای مولکولی دیگر (مانند CISH یا SISH) توصیه میشود.
✅ پس به طور استاندارد: - IHC 3+ → HER2 مثبت (نیاز به FISH ندارد).
- ولی در عمل، به دلیل احتمال موارد نادر false positive، گاهی مراکز مرجع باز هم برای تأیید از FISH استفاده میکنند.
در موارد 2+، برای تعیین دقیقتر، از روش مولکولی FISH استفاده میشود.
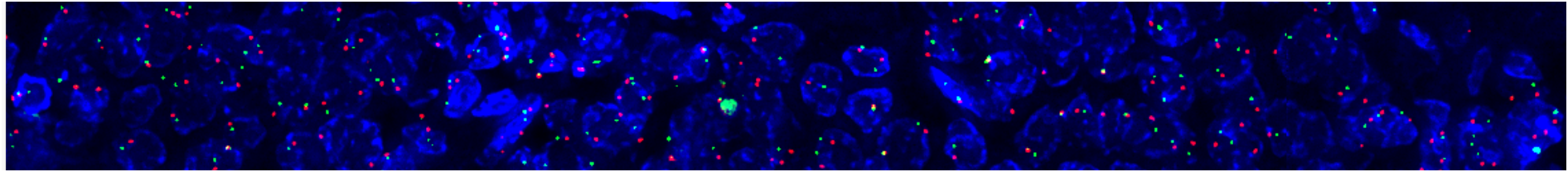
2.2. هیبریداسیون درجا با فلورسنس (FISH)
FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) یک روش مولکولی پیشرفته است که با استفاده از پروبهای DNA فلورسنت، میزان تکثیر ژن HER2 را در نمونه بافتی (بلوک پارافینه FFPE) اندازهگیری میکند.
نتایج FISH بهصورت زیر گزارش میشوند:
- Positive (Amplified): افزایش تعداد کپی ژن HER2 → تومور HER2 مثبت
- Negative (Non-amplified): تعداد کپی نرمال → تومور HER2 منفی
FISH در موارد مرزی (IHC 2+) روش استاندارد برای تعیین وضعیت نهایی HER2 است.
3. کاربردهای بالینی تست FISH برای HER2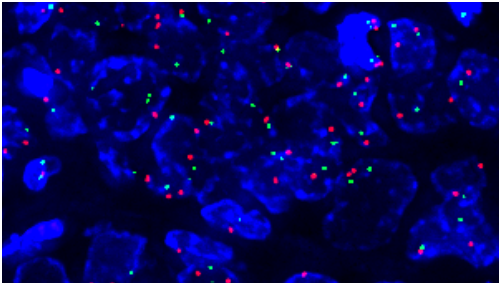
- تشخیص قطعی HER2 در موارد مشکوک (IHC 2+)
- انتخاب بیماران برای درمان با داروهای هدفمند ضد-HER2 مانند:
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
- Lapatinib
- Pertuzumab
- جلوگیری از درمانهای پرهزینه و پرعارضه در موارد HER2 منفی
4. مراحل انجام تست FISH HER2
4.1. نمونه مورد نیاز:
نمونه بافتی (FFPE) حاصل از بیوپسی یا جراحی پستان
4.2. مراحل آزمایش:
- برشگیری از بلوک پارافینه
- هیبریداسیون پروب FISH (مثلاً پروب CytoCell HER2/ERBB2)
- شستشو و رنگآمیزی با DAPI برای هسته
- بررسی با میکروسکوپ فلورسنت
4.3. تفسیر نتایج:
- نسبت HER2/CEP17 ≥ 2 یا تعداد کپی HER2 ≥ 6 → Amplified (مثبت)
- نسبت < 2 و کپی HER2 < 4 → non-amplified (منفی)
5. تفاوت FISH با سایر روشها (IHC و CISH)
ویژگیIHCFISHCISH
| نوع بررسی | پروتئینی | ژنتیکی | ژنتیکی |
| حساسیت | متوسط | بالا | متوسط |
| نوع رنگ | کروموژن | فلورسنت | کروموژن |
| نیاز به میکروسکوپ خاص | خیر | بله | خیر |
| کاربرد | غربالگری اولیه | تایید موارد مشکوک | جایگزین FISH در مراکز فاقد فلورسانس |
6. نقش HER2 در درمان و پیشآگهی
تومورهای HER2 مثبت:
- تهاجمیتر هستند
- پیشآگهی ضعیفتری دارند
- به درمانهای هدفمند پاسخ میدهند
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) اولین داروی هدفمند ضد-HER2 است که باعث بهبود بقاء در بیماران HER2 مثبت شده و اکنون در درمان سرطان پستان، معده و مری استفاده میشود. به دلیل عوارض قلبی و هزینه بالا، انجام تست FISH پیش از تجویز دارو الزامی است.
7. جمعبندی
تکنیک FISH HER2 یک روش تشخیصی دقیق و استاندارد در تایید وضعیت HER2 در سرطان پستان است. این تکنیک نقش اساسی در تعیین مسیر درمانی بیماران دارد و به ویژه در موارد IHC 2+ حیاتی است.
توصیه نهایی:
در بیماران مبتلا به سرطان پستان، تعیین دقیق وضعیت HER2 با استفاده از FISH نه تنها موجب انتخاب صحیح درمان میشود، بلکه از مصرف بیرویه داروهای گرانقیمت و پرعارضه جلوگیری میکند.
🔬 دلایل علمی احتمالی عدم وجود سيگنال خوب :
1. مشکلات مربوط به نمونه (پیشتحلیلی)
- فیکساسیون نامناسب: استفاده طولانی یا ناکافی از فرمالین باعث تخریب DNA و کاهش دسترسی پروب به توالی هدف میشود.
- نمونه قدیمی یا بافت بیش از حد فرمالینه: DNA شکسته شده و هیبریداسیون به خوبی رخ نمیدهد.
- ضخامت برش زیاد یا خیلی نازک: برشهای ضخیم باعث همپوشانی سیگنالها و برشهای خیلی نازک باعث کاهش DNA میشوند.
2. مشکلات در دناتوراسیون و هیبریداسیون
- دمای نامناسب دناتوراسیون: اگر دما پایینتر از حد لازم باشد → DNA کامل دناتوره نمیشود و پروب نمیتواند متصل شود. اگر خیلی بالا باشد → DNA تخریب میشود.
- زمان ناکافی یا بیش از حد هیبریداسیون: زمان کم → اتصال ناقص، زمان زیاد → کاهش سیگنال به علت شستشوی شدید یا کاهش استحکام هیبرید.
- خشک شدن پروب در حین هیبریداسیون: پروب باید در محیط مرطوب بماند، خشک شدن باعث از دست رفتن اتصال میشود.
3. مشکلات مربوط به پروب
- کیفیت پایین یا تاریخ انقضای پروب: فلوروفورهای پروبها با گذر زمان تخریب میشوند.
- ذخیرهسازی نامناسب پروب (نور، دما، انجماد-ذوب مکرر): این موارد باعث کاهش شدت فلورسانس میشوند.
4. مشکلات پس از هیبریداسیون (Post-hybridization)
- شستشوی بیش از حد یا در دمای بالا: سیگنالها از بین میروند.
- ماندن بافر روی اسلاید یا آلودگی: میتواند باعث کاهش کیفیت سیگنال شود.
- Bleaching (کاهش شدت فلورسانس): نور میکروسکوپ فلورسنت اگر زیاد و طولانی تابیده شود، سیگنالها محو میشوند.
5. مشکلات مربوط به میکروسکوپ و فیلترها
- فیلترهای فلورسنت قدیمی یا کثیف → عبور ناکافی نور فلوروفور.
- شدت لامپ یا LED پایین → سیگنال ضعیف دیده میشود.
📌 خلاصه:
وقتی DAPI خوب است ولی سیگنال پروب ضعیف یا صفر دیده میشود، معمولاً مشکل از هیبریداسیون پروب، کیفیت پروب یا شرایط دناتوراسیون/شستشو است، نه از کیفیت هستهها.
Also Known As: C-erbB-2, ERBB2, HER2/neu, HercepTest, Human EGF Receptor 2, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2Board Approved
Test Quick Guide
The HER2 test is a tumor marker test that determines the number of copies of the HER2 gene or the amount of HER2 protein in a cancer cell. It is performed on a tissue sample taken during a procedure called a biopsy.
For some types of cancer, including breast cancer, stomach cancer, and esophageal cancer, the results of HER2 testing help doctors estimate the course of the disease and plan treatment.
About the Test
Purpose of the test
The purpose of HER2 testing is to determine whether cancer cells have too many copies of the HER2 gene or a higher than normal level of the HER2 protein. Cancers with higher-than-normal levels of HER2 are called “HER2-positive.” Cancers with normal HER2 levels are called “HER2-negative.”
HER2 testing provides information about a patient’s prognosis, which relates to how the cancer is most likely to behave. HER2-positive cancers tend to be more aggressive. HER2 testing also determines whether a patient may benefit from treatment that is designed to target HER2 genes and/or proteins. This type of treatment is called targeted therapy.
What does the test measure?
HER2 tests can measure either the amount of HER2 protein on the surface of the cancer cell or the number of copies of the HER2 gene inside the cell.
HER2 is a protein involved in normal cell growth and development. However, cancer cells that have extra copies of the HER2 gene create too much of the HER2 protein. This extra HER2 protein can cause the cancer cells to grow and spread more quickly.
There are several laboratory techniques available to test for HER2. Methods that tests for the amount of HER2 protein on the cell surface include:
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Western blot
Methods that test for the number of copies of the HER2 gene in the cell include:
- In situ hybridization (ISH)
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
- Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)
- Silver-enhanced in situ hybridization (SISH)
- Differential polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
It is also possible to test the levels of HER2 protein that are circulating in the blood; however, this test is not widely used, and more research is needed to determine whether it can play a helpful role in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment planning.
When should I get a HER2 test?
HER2 testing is most often performed in the following individuals:
- Patients with newly diagnosed, invasive breast cancer
- Patients with breast cancer that has spread, also called metastatic breast cancer
- Patients with breast cancer that has come back after treatment, called recurrent breast cancer
- Patients with stomach or esophageal cancer that cannot be removed through surgery or that has recurred after treatment
HER2 testing may be recommended as part of the diagnostic work-up for other types of cancer. It may be helpful to ask your doctor about whether HER2 testing is appropriate for your diagnosis.
Finding a HER2 Test
How to get tested
HER2 testing is usually done on a tissue sample taken during a procedure called a biopsy. The sample is sent to a laboratory where a pathologist analyzes the tissue. Researchers are studying a blood test that measures HER2, but it is not widely used.
Can I take the test at home?
There is no at-home test for HER2. HER2 testing must be conducted on a tissue sample at a laboratory.
How much does the test cost?
The cost of HER2 testing varies and depends on a number of factors including insurance coverage, copays, deductibles, and laboratory or professional fees for the pathologist.
The cost of HER2 testing can also depend on the type of biopsy you receive and the type of laboratory method used to assess your HER2 status. If initial testing does not provide a clear result, additional HER2 testing can impact the cost as well.
It can be helpful to speak with your doctor or your insurance provider about the cost of HER2 testing. They can provide more information about expected out-of-pocket expenses for the biopsy and tissue analysis.
Taking a HER2 Test
A tissue sample is required for HER2 testing in most cases. Tissue is obtained during a procedure called a biopsy. There are different types of biopsy including needle biopsy, surgical biopsy, and endoscopic biopsy.
The type of biopsy you have will depend on a number of factors including the part of the body where your doctor takes a tissue sample. Your doctor can provide more information about what type of biopsy is best for your situation.
Before the test
Test preparation depends on the type of biopsy being recommended by your doctor. If your biopsy requires only a local anesthetic, there is generally no test preparation required.
If you need a surgical biopsy that requires general anesthesia or a sedative, you may be asked not to eat or drink for a period of time before the procedure. You will also need to ask someone to drive you home after your procedure if you will be undergoing general anesthesia or taking a sedative.
Regardless of the type of procedure being suggested, it is important to speak with your doctor about how to prepare for your biopsy.
During the test
During a biopsy, cells or tissue are removed so that they can be examined under a microscope. There are different types of biopsy procedures. Your doctor can tell you what type of biopsy procedure they recommend for your situation and what to expect.
In most cases, you will receive a local or general anesthetic. While there may be some pressure during the procedure if given a local anesthetic, you should not experience pain. If you receive a general anesthetic, you will be unconscious during the procedure and should not feel pain or pressure.
After the test
If you are having a needle biopsy, pressure will be applied to the biopsy site following the procedure to help stop any bleeding. The area will be covered with a sterile bandage.
For patients undergoing a surgical biopsy, the area where the tissue sample was removed will be closed with adhesive strips or stitches.
You may experience confusion or feelings of grogginess after waking from the procedure as a result of the anesthesia or sedative. Your doctor may recommend that you stay at the medical facility for observation and will provide you with instructions for recovering at home. Someone else will need to drive you home from your appointment.
HER2 Test Results
Receiving test results
The results of HER2 testing are included in a pathology report. Pathology reports are commonly sent to your doctor within 10 days of your biopsy procedure.
Your doctor may contact you directly to talk with you about the results and next steps. The report may also be posted to an online health portal or sent to you by mail.
Interpreting test results
A pathology report includes basic information that describes the tissue removed during the biopsy, the diagnosis, and the results of any additional testing performed on the tissue sample such as HER2 testing.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is often used on newly diagnosed invasive, metastatic, and recurrent breast cancer to determine HER2 status. IHC results for breast cancer are reported as follows:
- IHC 3+: HER2-positive
- IHC 2+: equivocal
- IHC 1+: HER2-negative
- IHC 0: HER2-negative
Results usually show that a tumor is clearly HER2-positive or HER2-negative. If the test does not show a clear result, a report may indicate that a result is “equivocal.” Follow-up testing after an equivocal result may be performed on the same tissue sample or a new tissue sample using in situ hybridization (ISH). ISH results are reported as either ISH-positive or ISH-negative.
A HER2-positive cancer diagnosis means that the cancer is likely to grow and spread more quickly and is more likely to recur. HER2-targeted treatments such as trastuzumab, pertuzumab or lapatinib may be part of the treatment plan for patients with HER2-positive cancer. If your tumor is HER2-negative, HER2-targeted therapies are not effective.
Are test results accurate?
HER2 testing is a common and important part of the diagnostic workup for patients with breast, gastric, and esophageal cancers. Like other laboratory and pathology tests, HER2 testing isn’t 100% accurate. There are several factors that can impact the accuracy of the test results:
- Laboratory methods: Because there are various methods to assess HER2 status, there can be variability in results depending on laboratory techniques and how the tumor sample is processed.
- Number of tumor samples tested: For patients with stomach cancer and some types of esophageal cancer, doctors may take multiple samples during a biopsy because a single sample may miss HER2-positive cancer cells. Some experts consider six to eight samples as an optimal number.
It is important to check with your doctor if you have any questions about your biopsy, the results, or the accuracy of testing used to evaluate the HER2 status of your tumor.
Do I need follow-up tests?
No specific follow-up testing is needed for those who undergo HER2 testing. However, if the results of an initial HER2 test do not clearly show whether the cancer is HER2-positive or HER2-negative, further HER2 testing is often performed to determine the HER2 status.
As you begin treatment for your cancer, your doctor may talk with you about a plan to monitor how treatment is going and how your cancer is responding to treatment. Talk with your doctor about what testing and follow-up is appropriate given your diagnosis.
Questions for your doctor about test results
You may find it helpful to ask your doctor the following questions to learn more about your HER2 test results and what they mean for your health:
- What are the results of my HER2 test? Am I HER2-positive or HER2-negative?
- What does the result of my test mean for my prognosis?
- How does my test result impact my treatment plan?
- Am I a candidate for HER2-targeted therapy?
How is HER2 testing different from testing for estrogen and progesterone hormone receptor status?
Estrogen and progesterone hormone receptor status, sometimes referred to as ER/PR status, is also evaluated as part of the initial work-up for patients with breast cancer. While HER2 testing looks for extra HER2 protein or genes, ER/PR testing looks for the presence of estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors inside of the cancer cell.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone will bind to cancer cells with these receptors and cause the cancer to grow. Testing for ER/PR status determines whether a patient with breast cancer may benefit from a type of treatment called hormone therapy.
Related Tests
- National Cancer Institute: Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient VersionLearn More
- National Cancer Institute: Gastric Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient VersionLearn More
- National Cancer Institute: Esophageal Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient VersionLearn More

دیدگاه خود را بنویسید